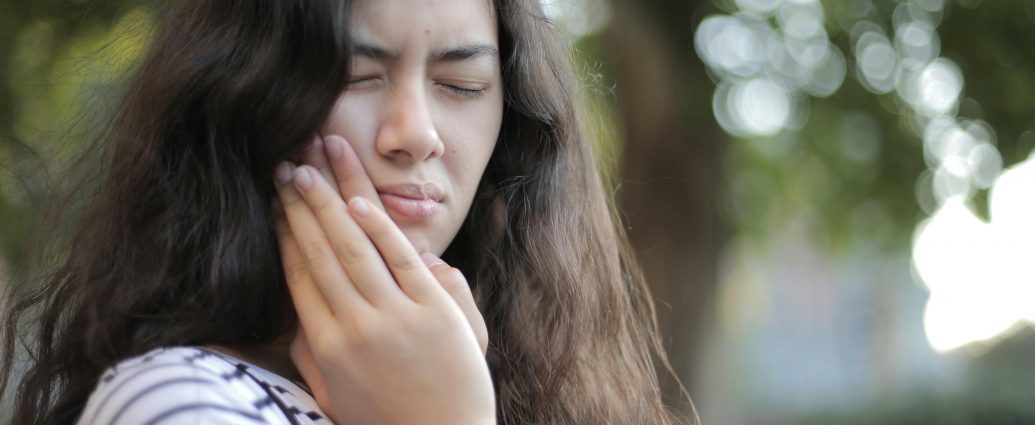
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders involve a range of issues affecting the jaw’s joint and surrounding muscles, leading to pain, discomfort, and functional impairment. The TMJ connects the jawbone to the skull and facilitates movements such as chewing, speaking, and yawning. When this joint or the surrounding muscles become problematic, it can significantly affect the quality of life.
Effective management of TMJ disorders involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining lifestyle modifications, therapeutic interventions, and, in some cases, surgical options. This article outlines key strategies for managing TMJ disorders.
Understanding TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders can result from several factors, such as jaw injury, teeth grinding (bruxism), arthritis, and stress. Symptoms often include jaw pain, headaches, difficulty moving the jaw, and clicking or popping sounds during jaw movement. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, patient history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Stress Management:
Stress is a common trigger for TMJ disorders. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and reduce muscle tension around the jaw.
Dietary Adjustments:
Consuming a soft diet can minimize jaw strain. Foods that require less chewing, such as soups, smoothies, and mashed potatoes, can alleviate discomfort. Avoiding hard, chewy, or sticky foods helps prevent exacerbating TMJ symptoms.
Jaw Exercises:
Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve jaw function and reduce pain. A physical therapist can guide you through appropriate exercises designed to enhance jaw mobility and alleviate muscle tension.
Therapeutic Interventions
Medications:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage TMJ pain. In some cases, a doctor might prescribe muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist specializing in TMJ disorders can provide targeted treatments, including ultrasound therapy, moist heat applications, and manual therapy. These methods help reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the TMJ.
Splints and Night Guards:
Dental splints or occlusal splints are custom-made devices worn over the teeth to prevent grinding and clenching. Night guards, specifically designed for nighttime use, can protect the teeth and reduce stress on the TMJ.
Heat and Cold Therapy:
Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can offer temporary relief from TMJ pain. Heat therapy helps to relax tight muscles, while cold therapy works to reduce inflammation and numb the discomfort.
Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections:
Botox London has emerged as a novel treatment for TMJ disorders, particularly when muscle tension and bruxism are involved. Botox works by temporarily paralyzing the muscles responsible for excessive jaw clenching and grinding. This can reduce pain, decrease muscle spasms, and improve overall jaw function. Botox injections are typically administered by a healthcare provider or dentist with experience in TMJ treatments. The effects generally last for several months, and repeat treatments may be necessary for ongoing relief.
Behavioral and Alternative Therapies
Biofeedback:
Biofeedback therapy helps individuals gain awareness and control over physiological functions. It can be useful in managing TMJ disorders by teaching patients how to regulate muscle tension and stress responses.
Acupuncture:
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique in which thin needles are inserted into specific points on the body. Acupuncture can help alleviate pain and promote healing by stimulating the body’s natural pain-relief mechanisms.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT can be beneficial for individuals with TMJ disorders related to stress and anxiety. This therapy helps patients identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to their symptoms.
Surgical and Invasive Options
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or if the TMJ disorder is severe, surgical intervention might be considered. Potential surgical options include:
Arthrocentesis:
This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting fluid into the joint space to wash out debris and reduce inflammation. It can provide temporary relief and improve joint function.
Arthroscopy:
A surgical technique where a small camera and instruments are inserted into the joint through tiny incisions. Arthroscopy allows for the removal of damaged tissue or repair of joint structures.
Open-Joint Surgery:
In rare cases, when other treatments are ineffective, open-joint surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves making a larger incision to access and repair or replace the damaged joint.
Preventive Measures
Good Oral Hygiene:
Maintaining healthy teeth and gums can prevent issues related to dental misalignment, which can contribute to TMJ disorders.
Avoiding Excessive Jaw Movements:
Minimizing activities that place excessive stress on the jaw, such as chewing gum or grinding teeth, can help prevent TMJ issues.
Regular Dental Check-Ups:
Regular visits to the dentist can help identify and address any issues with jaw alignment or bite problems before they develop into more significant TMJ disorders.
In Summary
Effective management of TMJ disorders requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s specific needs. By combining lifestyle changes, therapeutic interventions, and, if necessary, surgical options, patients can find relief from TMJ symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. If you suspect you have a TMJ disorder, consult with a healthcare provider or dental specialist who can help you determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your condition.

